-
Per GS1's EPC Tag Data Standard (TDS),the TID memory bank (MB10) of an EPC/RFID chip shall contain an 8 bit ISO/IEC 15963 allocation class identifier of E2h at memory locations 00h to 07h
-
RFID Tag Choice Can Make or Break Your Passive UHF Tracking Project RFID tag choice is critical to the success of your tracking project. There are many good, solid, money-saving, efficiency-making, data-rich, automagical reasons for using a passive ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID tracking system in your operations – none of which you will be able to realize if you choose the wrong RFID tag. “In our project requirements discussions, we spend as much time determining what tag the customer needs as we do on multiple other components combined,” explains Richard Bissonnette, president of Strategic Systems and our resident RFID tag expert. “If you select a tag randomly or because you like the way it looks, but it doesn’t have enough memory or durability – just flat-out doesn’t meet the reality of what you&rsquo...
-
RFID technology has been widely deployed for asset tagging in a variety of industrial and government settings. The typical application uses a serialized set of tags with encoded EPC memory and a database, which links the EPC data of the tag to an asset identifier. For example, an RFID tag encoded with a 96 bit EPC code may be associated with a specific serial number computer server, machine tool or medical device. Implicit in the tracking system design is the assumption that the tag can be reliably read and, thus, the asset correctly identified. This process, however, can be compromised with a problem known as bit-flipping. BIT-FLIPPING The vast majority of RFID tags in the marketplace utilize EEPROM memory to store the identification data. Charge stored in memory cells determine the value of each bit in the identifying EP...
-
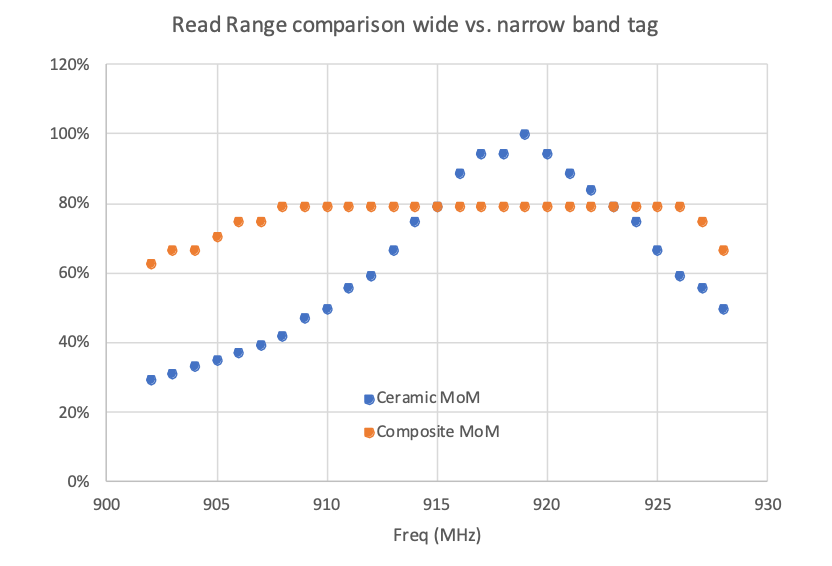
RFID tag performance is traditionally evaluated based on read range. But another factor plays just as big of a role and is often overlooked: bandwidth. Most sellers and users of RFID tags only characterize tag performance by one factor: read range. There are situations where it makes since for read range to be a shorthand for tag performance. But response bandwidth that can have a significant effect on a tag’s performance in real world applications. Overlooking it can cost you read range and performance. RFID FREQUENCY BANDS RFID readers in North America operate in the 902-928 MHz frequency band. The readers ‘frequency hop’ within this band, changing frequencies at random. The purpose of this hopping is to avoid interference with other readers in the vicinity. Frequency bandwidth is the ability of a component to respond to signa...